Infrastructure: Could smart-tracking solve Auckland’s congestion problems? (NZ Herald)
Singapore aims to have the world’s most advanced road pricing system by 2020.
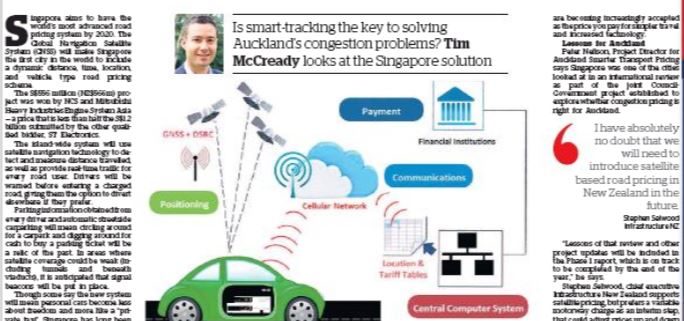
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) will make Singapore the first city in the world to include a dynamic distance, time, location, and vehicle type road pricing scheme.
The S$556 million (NZ$566m) project was won by NCS and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Engine System Asia – a price that is less than half the S$1.2 billion submitted by the other qualified bidder, ST Electronics.
The island-wide system will use satellite navigation technology to detect and measure distance travelled, as well as provide real-time traffic for every road user. Drivers will be warned before entering a charged road, giving them the option to divert elsewhere if they prefer.
Parking information obtained from every driver and automatic streetside carparking will mean circling around for a carpark and digging around for cash to buy a parking ticket will be a relic of the past.
In areas where satellite coverage could be weak (including tunnels and beneath viaducts), it is anticipated that signal beacons will be put in place.
Though some say the new system will mean personal cars become less about freedom and more like a “private taxi”, Singapore has long been ahead of the world in road user charging.
In 1998 – when Auckland was suffering from a five-week power outage in the CBD caused by multiple power cables failing – Singapore was rolling out what was then the most sophisticated urban congestion charging system on the planet.
This gantry-based electronic road-pricing system targets roads that are heavily congested, and mostly operate at peak times, applying prices to achieve a minimum “level of service”.
Though some privacy concerns have been raised around the level of surveillance that comes with tracking all road users, there are similar issues with other forms of modern transport.
A push for alternative transport
Despite Singapore moving towards a sophisticated and expensive road pricing system, car ownership is low by global standards. This is largely due to the hefty price of a certificate of entitlement – S$36,000 (NZ$36,790) for cars up to 1600cc – which allows the certificate holder to register, own and use a vehicle in Singapore for a period of 10 years.
When you consider 12 per cent of the small country’s land area is consumed by roads, it is unsurprising that Singapore’s Minister for Infrastructure and Transport, Khaw Boon Wan, has set a target for 75 per cent of trips to take place by public transport by 2030, and 85 per cent by 2050.
Singapore is also significantly boosting its bus fleet, rail network, cycling paths, and the distance of its covered walkways.
Driverless cars are tipped to be a further game-changer. Singapore’s well-maintained roads and contained geography make it an ideal location for autonomous vehicles, expected to offer greater fuel efficiency, reduced road congestion and carbon emissions, and a significant reduction in accidents.
Last year US autonomous vehicle R&D firm nuTonomy ran a limited public trial for the world’s first driverless taxis in Singapore.
Despite one of nuTonomy’s self-driving cars hitting a truck, the trial was considered a success.
The company noted the accident was due to “an extremely rare combination of software anomalies,” and intends to launch a commercial service in Singapore in the next year.
It is therefore not unthinkable that at some point, mass use of driverless cars and public transport could remove the need for congestion charging altogether.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!